Removable Device Developed for Treatment of Type I Diabetes
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 18 Jan 2018
A team of biomedical engineers has devised a novel technique for implantation and removal of living pancreatic beta cells in order to control insulin levels in patients with type I diabetes.Posted on 18 Jan 2018
Cell encapsulation has been shown to hold promise for effective, long-term treatment of type I diabetes. However, various obstacles have delayed the adaptation of this approach for clinical applications. For example, there is an unmet need for an encapsulation system that is capable of delivering sufficient cell mass while still allowing convenient retrieval or replacement.
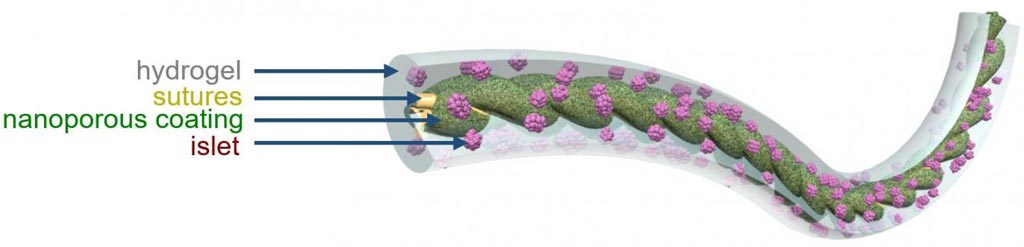
Image: An illustration of TRAFFIC (Thread-Reinforced Alginate Fiber for Islets enCapsulation), a novel removable implant device for control of type I diabetes (Photo courtesy of Cornell University).
To fill this gap, investigators at Cornell University (Ithaca, NY, USA) developed a simple cell encapsulation system that is readily scalable and conveniently retrievable. The key to this design was to engineer a highly wettable, Ca2+-releasing nanoporous polymer thread that promoted uniform in situ cross-linking and strong adhesion of a thin layer of alginate hydrogel around the thread. This method – named TRAFFIC (Thread-Reinforced Alginate Fiber for Islets enCapsulation) by the investigators - was used to implant hundreds of thousands of islet cells into animal diabetes models. The cells were protected by a thin hydrogel coating and the coated cells were attached to a polymer thread that could be removed or replaced easily when the cells had outlived their usefulness.
Results published in the December 26, 2017, online edition of the journal Proceedings of the [U.S.] National Academy of Sciences revealed that the device provided immunoprotection of rat islets in immunocompetent C57BL/6 mice in a short-term (one-month) study, similar to neat alginate fibers. However, the mechanical property of the device, critical for handling and retrieval, was much more robust than the neat alginate fibers due to the reinforcement of the central thread. It also had facile mass transfer due to the short diffusion distance.
The investigators demonstrated the therapeutic potential of the device through the correction of chemically induced diabetes in C57BL/6 mice using rat islets for three months as well as in immunodeficient SCID-Beige mice using human islets for four months. They further showed, as a proof of concept, the scalability and retrievability of the device in dogs. After one month of implantation in dogs, the device could be rapidly retrieved through a minimally invasive laparoscopic procedure.
"The ability to remove the transplant is key because of its potential to form tumors," said senior author Dr. Minglin Ma, assistant professor biological and environmental engineering at Cornell University. "When they fail or die, they need to come out. You do not want to put something in the body that you cannot take out. With our method, that is not a problem."
Related Links:
Cornell University













