Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Effectiveness Dependent on HLA Diversity
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 26 Dec 2017
Findings reported in a recently published paper suggested that an individual’s own genes controlled his or her response to immunotherapy drugs known as immune checkpoint inhibitors.Posted on 26 Dec 2017
Immune checkpoints are immune system molecules, which can be either stimulatory or inhibitory, that affect immune system function. Tumors can use these checkpoints to protect themselves from immune system attacks. Currently approved checkpoint therapies block inhibitory checkpoint receptors. Blockade of negative feedback signaling to immune cells thus results in an enhanced immune response against tumors. However, not all patients respond to this type of immunotherapy.
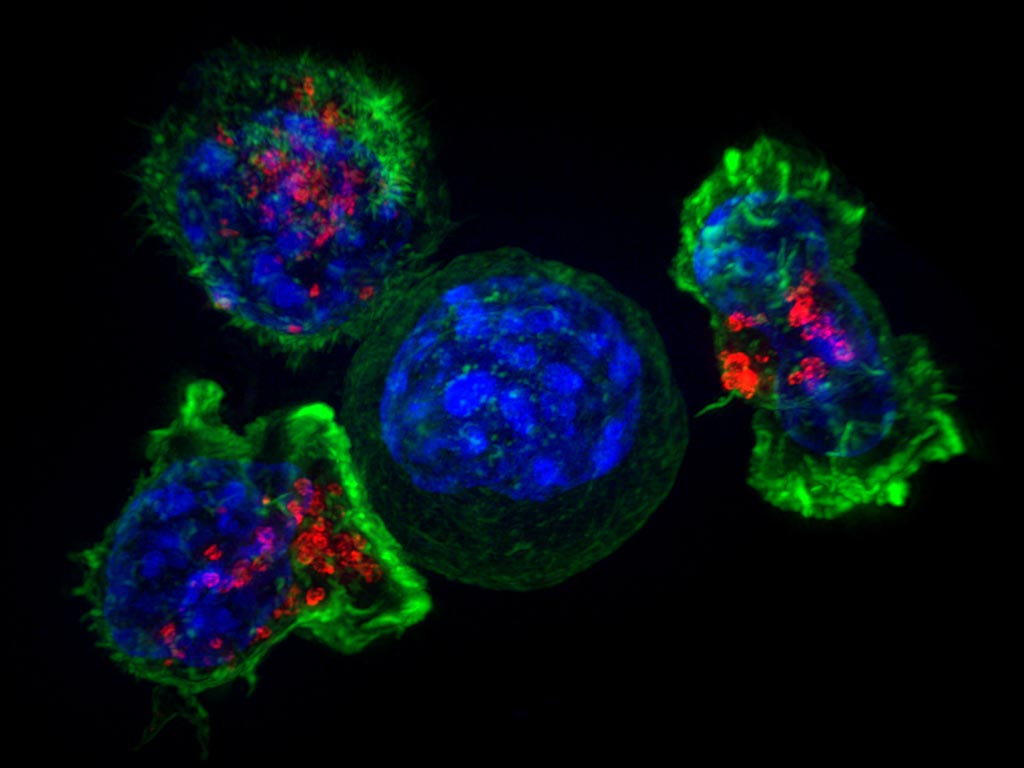
Image: Three T-cells surround a cancer cell. New drugs, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, can help the immune system attack cancer, but the drugs’ effectiveness depends on the patient’s genetic makeup (Photo courtesy of the U.S. National Institutes of Health).
Investigators at the Columbia University Medical Center (New York, NY, USA) looked for an explanation for this failure. To this end, they conducted a study involving 1,535 cancer patients who had been treated with checkpoint inhibitors.
They reported in the December 7, 2017, online edition of the journal Science that patients who had more versions (a greater diversity) of HLA (human leukocyte antigen) genes responded better to the therapy. Furthermore, patients with a combination of low HLA diversity and fewer tumor mutations did not respond as well to immune checkpoint inhibitors. The (HLA) system is a gene complex that encodes proteins that the immune system uses to recognize which cells belong in the body and those that are foreign.
“Some HLA genes have hundreds of different versions; however there previously was little understanding of the relationship between an individual’s HLA composition and response to checkpoint inhibitors,” said senior author Dr. Naiyer Rizvi, professor of medicine at Columbia University Medical Center. “The relationship between HLA and outcomes to immune checkpoint inhibitors is important for many reasons. It is another piece of the immunotherapy puzzle–who responds and why. It also may be relevant for understanding side effects observed with immunotherapy, and this is an area we are currently exploring.”
Related Links:
Columbia University Medical Center













