Novel Immunotherapy Approach Shrinks or Eliminates Advanced Tumors
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 03 Nov 2016
A novel four-component approach to anti-cancer immunotherapy overcame the complex network of immunosuppressive pathways present in advanced tumors and caused shrinkage of several types of tumors in different mouse models.Posted on 03 Nov 2016
Up to now attempts to treat tumors with immunotherapy have had only limited success probably due in part to the complex network of immunosuppressive pathways present in advanced tumors, which are unlikely to be overcome by intervention at a single signaling checkpoint.
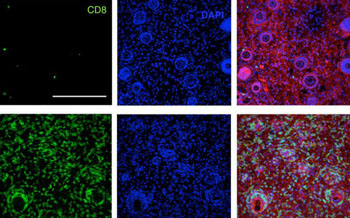
Image: In this image, the top row shows few T-cells in untreated mice, while the bottom rows show many T-cells produced after immunotherapy treatment (Photo courtesy of Massachusetts Institute of Technology).
To deal with these multiple pathways, investigators at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Cambridge, USA) developed a combination immunotherapy approach that recruited a variety of innate and adaptive immune cells. The treatment comprised four parts: an antibody targeted to the tumor, a vaccine targeted to the tumor; the cytokine interleukin-2 (IL-2), and a molecule that blocked the programmed cell death 1 (PD1) protein, a receptor found on T-cells. Each component had a critical role to perform. The antibodies stimulated the recruitment of additional immune cells that helped to activate T-cells; the vaccine stimulated proliferation of T- cells to attack the tumor; IL-2 prompted the T-cell population to expand quickly; and the anti-PD1 molecule extended T-cell activity.
The investigators tested this combination treatment in mice that had been implanted with three different types of tumors: melanoma, lymphoma, and breast cancer. They reported in the October 24, 2016, online edition of the journal Nature Medicine that about 75% of the well-established tumors in all strains of experimental mice were completely eliminated. Furthermore, six months later, the immune systems of these mice retained the ability to completely clear freshly injected tumor cells.
"We have shown that with the right combination of signals, the endogenous immune system can routinely overcome large immunosuppressive tumors, which was an unanswered question," said senior author Dr. Darrell Irvine, professor of biological engineering and of materials science and engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. "We had this really good lymph-node-targeting vaccine that will drive very strong adaptive immunity, and they had this combination that was recruiting innate immunity very efficiently. We wondered if we could bring these two together and try to generate a more integrated immune response that would bring together all arms of the immune system against the tumor."
Related Links:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology













