Naturally Occurring CRISPR/Cas9 Cuts DNA and RNA
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 13 Mar 2018
A team of molecular microbiologists has identified a naturally occurring version of the CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing complex that cuts both DNA and RNA with equal proficiency.Posted on 13 Mar 2018
CRISPR/Cas9 is regarded as the cutting edge of molecular biology technology. CRISPRs (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) are segments of prokaryotic DNA containing short repetitions of base sequences. Each repetition is followed by short segments of "spacer DNA" from previous exposures to a bacterial virus or plasmid. Since 2013, the CRISPR/Cas9 system has been used in research for gene editing (adding, disrupting, or changing the sequence of specific genes) and gene regulation. By delivering the Cas9 enzyme and appropriate guide RNAs (sgRNAs) into a cell, the organism's genome can be cut at any desired location. The conventional CRISPR/Cas9 system is composed of two parts: the Cas9 enzyme, which cleaves the DNA molecule and specific RNA guides that shepherd the Cas9 protein to the target gene on a DNA strand.
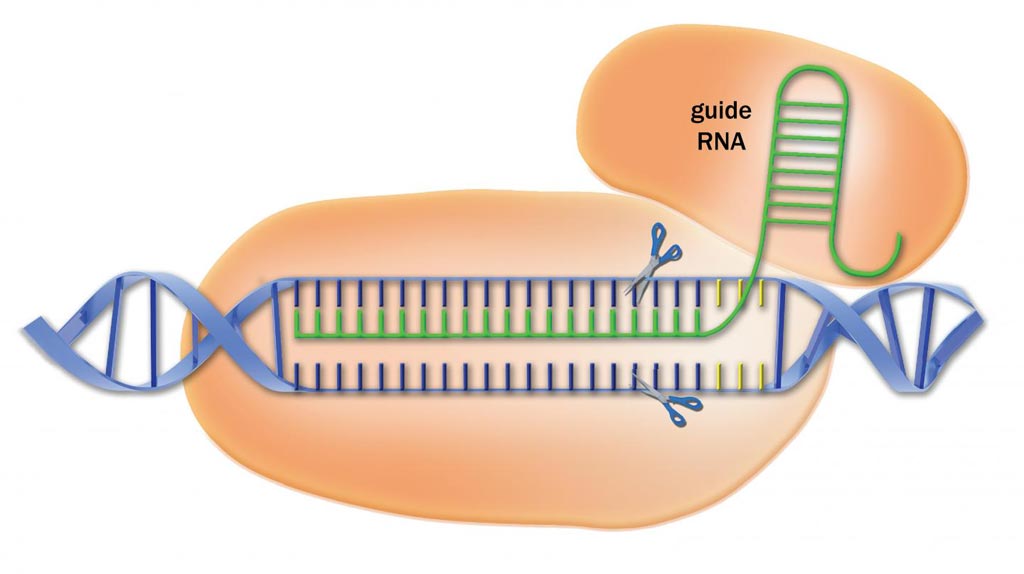
Image: CRISPR/Cas9 is a reprogrammable DNA cutting machine that is being used to edit genomes in many organisms for research purposes (Photo courtesy of Advanced Analytical Technologies).
While recent work has shown that some Cas9 nucleases can also target RNA, RNA recognition has required nuclease modifications or accessory factors. Nonetheless, in a study published in the March 1, 2018, issue of the journal Molecular Cell investigators at the University of Würzburg (Germany) reported that the Campylobacter jejuni Cas9 (CjCas9) could bind and cleave complementary endogenous mRNAs.
"We continue to be amazed by what Cas9 is capable of doing and what new applications and technologies these insights create," said senior author Dr. Cynthia Sharma, professor of molecular infection biology at the University of Würzburg. "The protein is also capable of cutting related molecules, called ribonucleic acids - RNA, for short. Not only that, but we found that we could also program this Cas9 to target and cut specific RNA molecules."
Related Links:
University of Würzburg













