Alternative Technique Developed for Toxicity Screening
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 20 Sep 2017
An innovative high-throughput screening technique is expected to improve drug development strategies by greatly reducing the time required to identify the potential for expression of toxic side effects.Posted on 20 Sep 2017
Currently, the potential for a candidate drug compound to induce toxic side effects is evaluated by its activation of key "reporter genes" – a cellular-based analytical process that can require 24 hours or more.
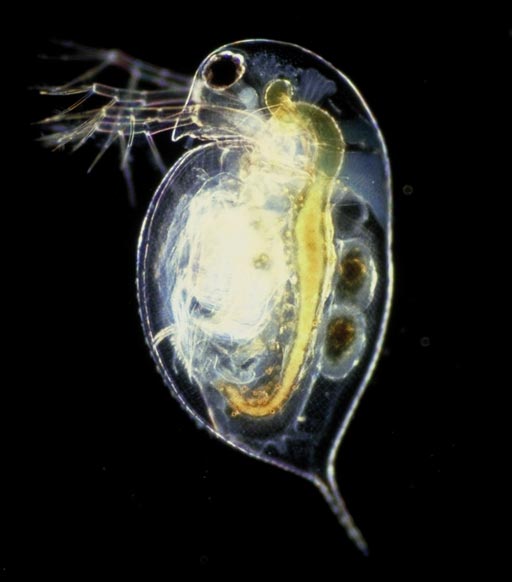
Image: The water flea Daphnia pulex, source of the MfR protein subunits Met and SRC (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons).
To speed up this process, investigators at North Carolina State University (Raleigh, USA) developed a modified version of the BRET (bioluminescence resonance energy transfer) method. This approach, which took only a few seconds, measured a cellular response that appeared when the drug candidate bound to a target protein, which caused the target protein to recruit other proteins.
In this specific application, the investigators utilized BRET to detect and quantify the assembly of the methyl farnesoate receptor (MfR) in response to various high-production volume and other chemicals. The hormone methyl farnesoate bound to the MfR to regulate various aspects of reproduction and development in crustaceans. The MfR protein subunits Met and SRC, cloned from the water flea Daphnia pulex, were fused to the fluorophore, mAmetrine and the photon generator, Rluc2, respectively.
The investigators reported in the July 14, 2017, online edition of the journal Environmental Science & Technology that ligand-mediated receptor assembly was measured by photon transfer from the photon donor to the fluorophore resulting in fluorescence emission. Overall, the BRET assay had comparable or greater sensitivity as compared to a traditional reporter gene assay.
"This new approach can help us identify chemicals that are more likely to pose an environmental hazard and, therefore, should be prioritized for testing. And this technique could also be used to assess and prioritize chemicals for human toxicity testing," said senior author Dr. Gerald LeBlanc, professor of biological sciences at North Carolina State University. "If we introduce a chemical to the system, we can tell almost instantaneously whether the chemical has stimulated the recruitment of SRC to Met, and by measuring the intensity of the light, we can also assess the potency of the chemical to activate this pathway. Because the Met-SRC complex regulates a gene that controls reproductive development in crustaceans, we know that such activity means there is a significant likelihood of environmental toxicity, enough to make it a priority for in-depth toxicity testing. This is an approach that could be applied to a wide variety of potential target proteins for virtually any species, and could significantly expedite screening of chemicals for prioritization."
Related Links:
North Carolina State University













