Review Article Summarizes Progress Towards Drug Development
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 02 Apr 2018
A recent review article summarized the methods used to identify new inhibitors for amino acid transporters and outlined cell and organ function where these can be used to modulate, prevent, or to treat diseases.Posted on 02 Apr 2018
Amino acids perform a variety of functions in cells and organisms, particularly in the synthesis of proteins, as energy metabolites, neurotransmitters, and precursors for many other molecules. Amino acid transport plays a key role in all these functions. Inhibition of amino acid transport is being pursued as a therapeutic strategy in several areas, such as diabetes and related metabolic disorders, neurological disorders, cancer, and stem cell biology. The role of amino acid transporters in these disorders and processes is well established, but the implementation of amino acid transporters as drug targets is still in its infancy. This is at least in part due to the underdeveloped pharmacology of this group of membrane proteins.
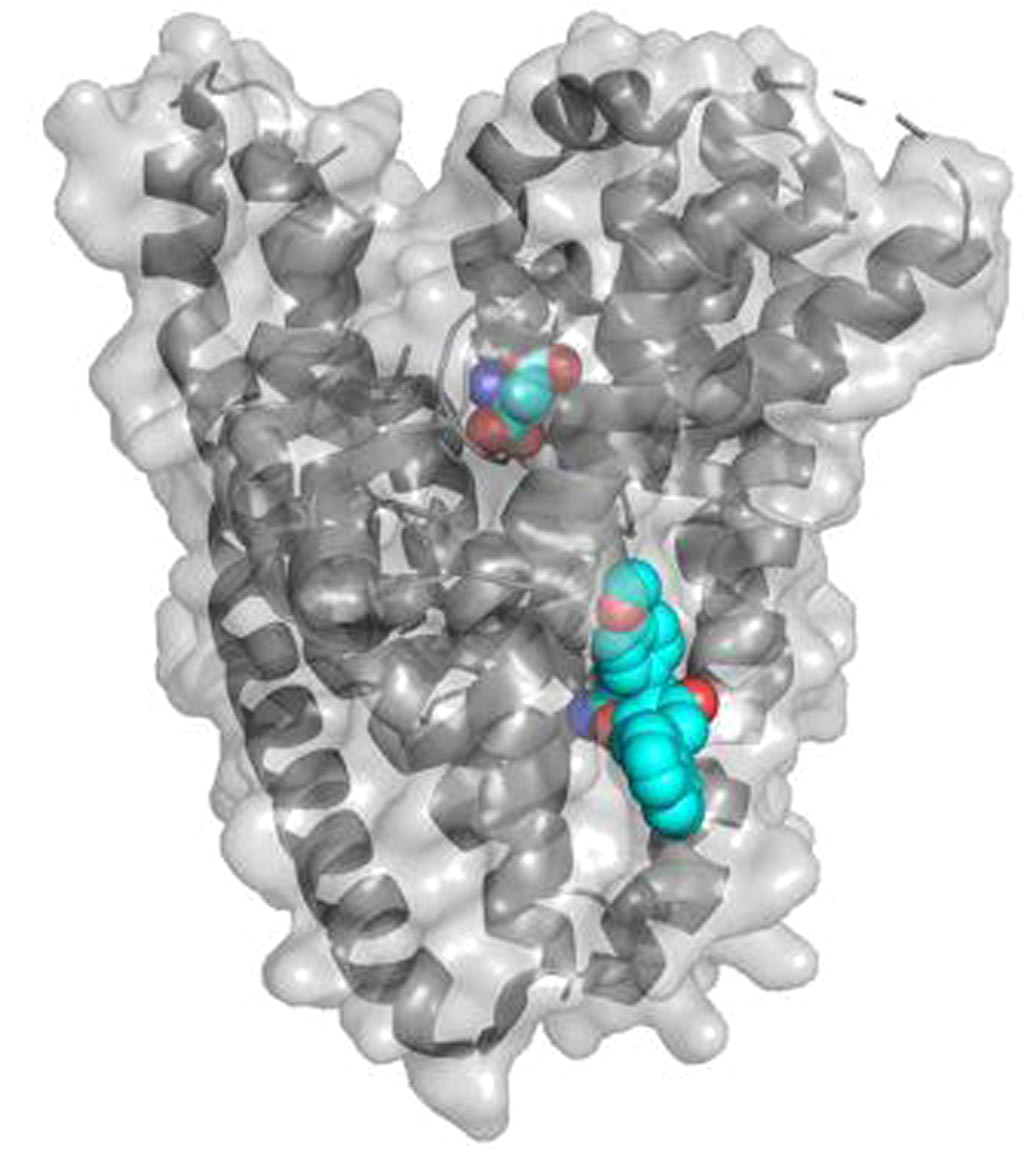
Image: The binding site of the amino acid transporter inhibitor UCPH101 was resolved by X-ray crystallography and was located at a distance from the substrate-binding site. In the image, the substrate is shown in the center of the transporter, while the inhibitor is located between the translocation and scaffold domain of the transporter (lower right). The inhibitor glues the two domains together, thereby inhibiting transport (Photo courtesy of Dr. Stefan Broer).
In a review article published in the March 20, 2018, online edition of the journal SLAS Discovery, Dr. Stefan Broer, professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at the Australian National University (Acton, Australian Capital Territory) discussed the demand for better inhibitors of amino acid transport processes and emphasized promising new strategies and targets for developing amino acid transporters as drug targets. Topics covered in the review included: (1) principles of transporter inhibition, (2) methods to identify transporter inhibitors (including scintillation proximity assays, biosensors, and mass spectrometry), and (3) the role of transporters in nutritional, neurological, and immune disorders as well as cancer.
Dr. Boer concluded the review by saying, "Recent advances in structural biology, membrane protein expression, and inhibitor screening methodology will see an increased number of improved and selective inhibitors of amino acid transporters that can serve as tool compounds for further studies."
Related Links:
Australian National University













