Novel Method Extends Range of Bacteriophage-based Applications
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 04 Jul 2017
A team of Israeli molecular microbiologists developed a method for extending the host specificity of bacteriophage particles to enable them to transfer DNA into a wide range of pathogenic bacteria.Posted on 04 Jul 2017
A major limitation in using bacteriophage-based applications is their narrow host range. Approaches for extending the host range have focused primarily on lytic phages in hosts supporting their propagation rather than approaches for extending the ability of DNA transduction into phage-restrictive hosts.
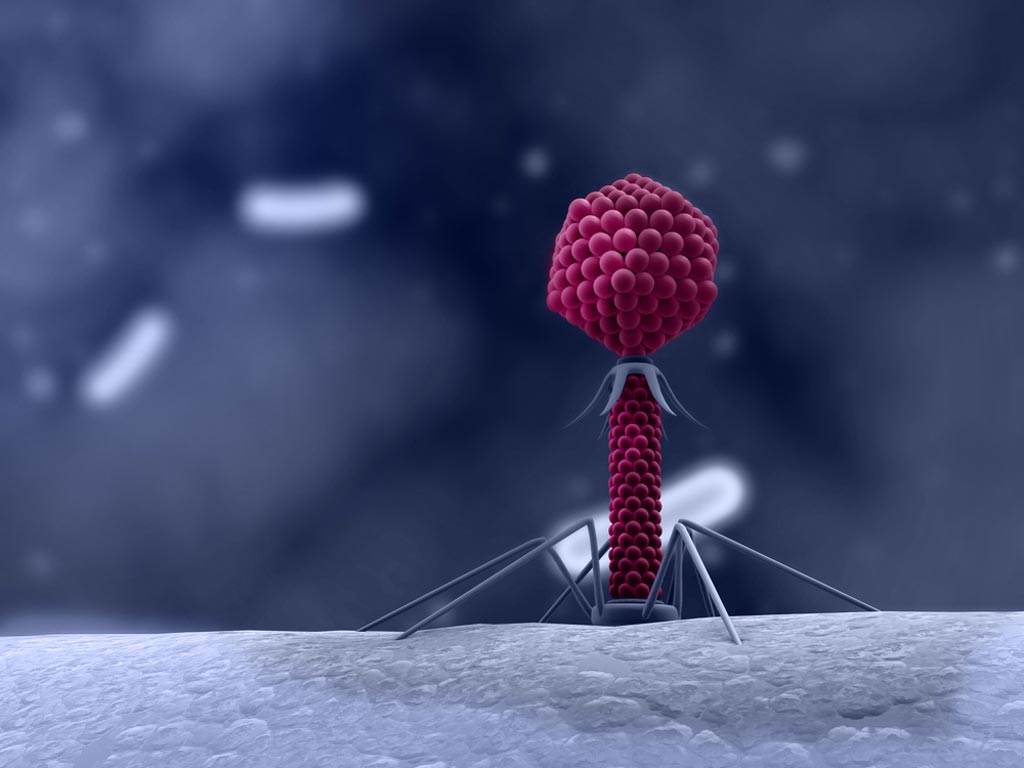
Image: Researchers have developed hybrid bacteriophage particles that could broaden the range of target bacteria (Photo courtesy of Tel Aviv University).
To extend the host range of T7 phage for DNA transduction, investigators at Tel Aviv University (Israel) designed a novel class of hybrid particles that displayed various bacteriophage tail/tail fiber protein combinations. The investigators programmed these modular particles to package and transduce DNA into hosts that normally restricted T7 phage propagation.
The investigators also developed an innovative generalizable platform that considerably enhanced DNA transfer into new hosts by artificially selecting tails that efficiently transduced DNA. In addition, they demonstrated that the hybrid particles were able to transduce desired DNA into desired hosts.
"DNA manipulation of pathogens includes sensitization to antibiotics, killing of pathogens, disabling pathogens' virulence factors, and more," said senior author Dr. Udi Qimron, professor of clinical microbiology and immunology at Tel Aviv University. "We have developed a technology that significantly expands DNA delivery into bacterial pathogens. This may indeed be a milestone, because it opens up many opportunities for DNA manipulations of bacteria that were impossible to accomplish before. This could pave the way to changing the human microbiome - the combined genetic material of the microorganisms in humans - by replacing virulent bacteria with a-virulent bacteria and replacing antibiotic-resistant bacteria with antibiotic-sensitive bacteria, as well as changing environmental pathogens. We have applied for a patent on this technology and are developing products that would use this technology to deliver DNA into bacterial pathogens, rendering them a-virulent and sensitive to antibiotics."
The bacteriophage study was published in the June 1, 2017, issue of the journal Molecular Cell.
Related Links:
Tel Aviv University













